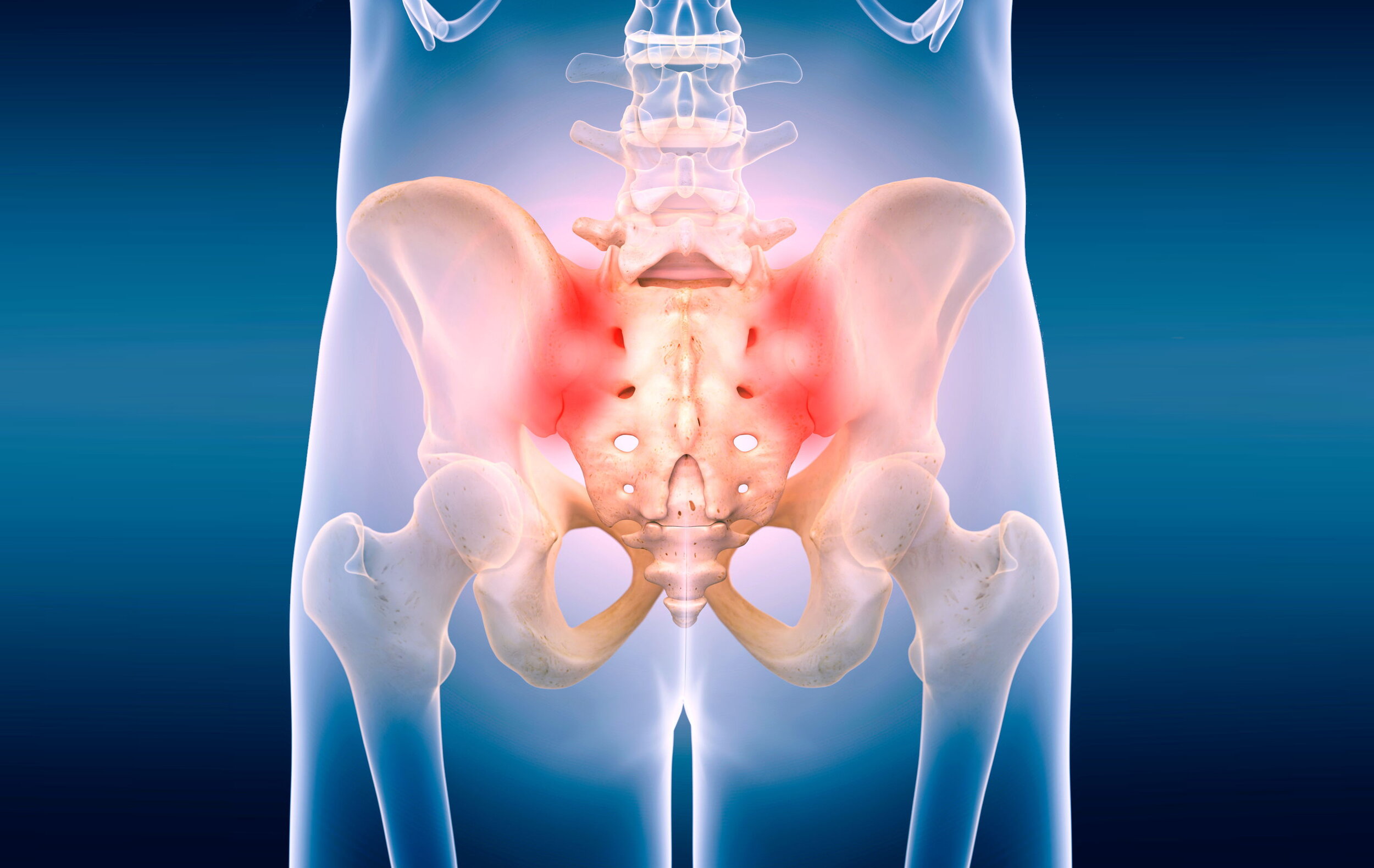
Sacroiliac Joint Anatomy
The SI joint is located between the sacrum and pelvic bones. The sacrum is the tailbone, which is in the middle and at the bottom of the lumbar spine. The tailbone attaches to the waist bones (or ilium), one on each side. So, in total there two sacroiliac joints, one on each side of the tailbone. One or both may be affected at one time in any given person.
At Aptiva Health, we offer same-day and walk-in appointments for spine injuries and conditions to evaluate, diagnose, and make the appropriate referral for additional treatment based upon your specific spine injury or condition. We treat spine injuries and conditions in our Spine, Pain Management, General Medicine, Orthopedics, and Physical Therapy departments.
Sacroiliac Joint as a Pain Source
The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) should not be overlooked as pain source. It is a very common source of low back pain, and many times is misdiagnosed as a problem with the discs or the spine. The sacroiliac joint may be responsible for almost 20 to 25% of all low back pain problems. Like other causes of low back pain, there are some patterns and symptoms associated with SIJ pain, also known as SIJ dysfunction or sacroiliitis.
These may include pain in one or all of the following areas on one or both sides of the body:
Back, Buttock, Hip, Groin or Thigh Pain
Discomfort while sitting for long periods of time
Difficulty with changing positions from sitting to standing, or vice versa
Associated with certain rheumatologic conditions (SLE, ankylosing spondylitis, etc.)
May be more common in females, during and/or after pregnancy
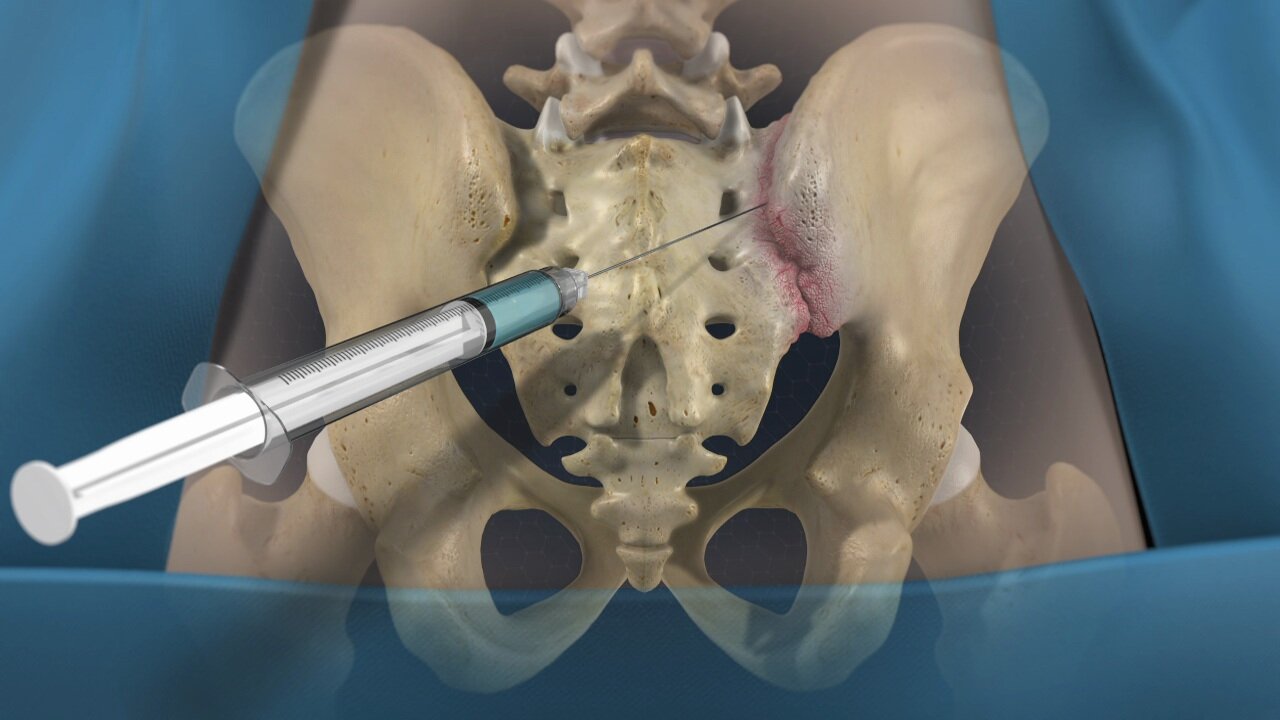
Sacroiliac (SI) joint pain is easily confused with back pain from the spine. Sometimes injecting the SI joint with lidocaine may help your doctor determine whether the SI joint is the source of your pain. If the joint is injected and your pain does not go away, it may be coming from a different source.
How is the procedure performed?
During the procedure, a mixture of local anesthetic and steroid is injected into the SI joint. The local anesthetic will numb the area, and steroid may help lower the swelling. The steroid should reduce the pain and improve the motion in your hip or buttock.
Will the injection hurt?
Your doctor will inject the medication and numbness scan over your hip joint. You may feel some stinging from the needle or the numbing medication. You may also fill some pressure or an increasing in your normal level of pain while the contrast dye, and then steroid mixed with local anesthetic is being injected. The temporary increase in pain may last for a few days after the procedure, until the steroid starts to work. The injection will take less than 10 minutes to complete.
How long does the effect last?
The injection usually gives temporary relief for several weeks or months at a time. If the pain goes away immediately, it confirms that the joint is the pain generator and the added steroid is to treat inflammation in the joint to provide pain relief SI joint injections can be used both to treat pain and to determine the source of the pain. This injection usually requires the use of fluoroscopic guidance or ultrasound in order to make sure the needle is placed correctly in the joint.
What is the next step after the injection?
You will be given a pain log to complete after the procedure. This will help us to measure your response to the injection and determine the next most appropriate plan of care. Please bring your pain log with you to your follow up appointment. In rare cases, the sacroiliac joint may need to be operated on or the nerves which supply the joint may need to be treated in order to eliminate the pain signals which are causing the pain to begin with.
What are the risks and side effects?
Serious side effects and complications are rare. The most common problem after the injection is having pain in the area of the injection for a few days. The other complications are infection, bleeding and nerve injury. These complications are minimized by stopping blood thinners, using sterile technique, and fluoroscopy for x-ray needle guidance.